Anterior shoulder dislocation
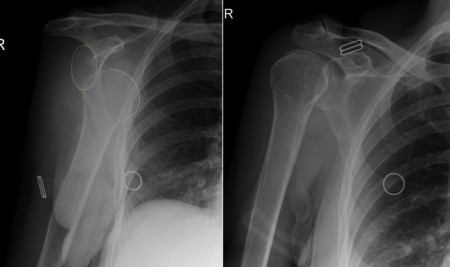
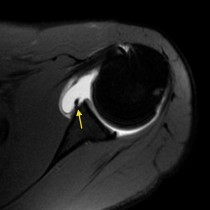
Anterior shoulder dislocation. The vast majority (>90%) of glenohumeral dislocations are anterior, as in this example (the glenoid is outlined by the yellow oval, the humeral head by the white curved line). Most of the remainder are posterior, and are typically associated with seizures. The image on the right in this case shows the same patient immediately following reduction of the dislocation in the ED. A post-reduction film is also performed – to ensure that the joint is truly reduced, and to assess for any associated fractures which may have been obscured on the first images. Potential fracture sites include the greater tuberosity, and the anteroinferior rim of the glenoid, as these bones tend to impact against each other when dislocation occurs. Fractures of these structures are called ‘Hill-Sachs’ and ‘Bankart’, respectively.