ARDS
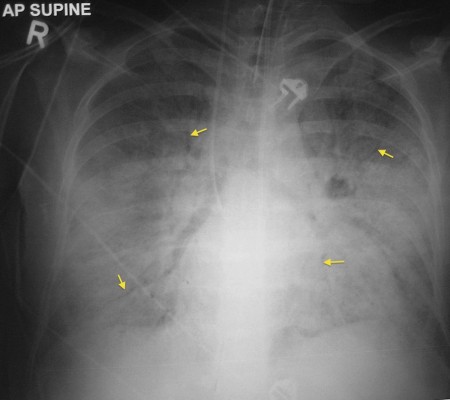
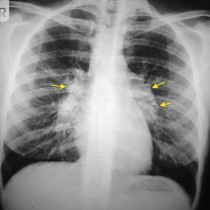
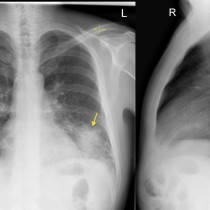
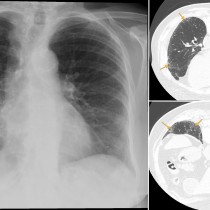
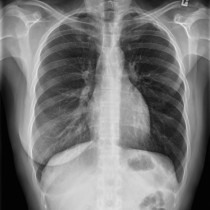
ARDS. This ICU patient has adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). The typical radiographic appearance of ARDS is bilateral widespread, confluent alveolar consolidation, often with prominent air bronchograms as in this case (arrows). It can be difficult to distinguish from pulmonary oedema – the absence of cardiomegaly is a helpful sign however most patients with ARDS will have had a portable AP radiograph, because they’re so ill, and so it can be difficult to assess the heart size. In ARDS there may be pleural effusions, but Kerley B lines are typically absent. This patient is intubated and has a right IJV line – don’t forget to check for complications related to this hardware, especially pneumothorax (not present here).