Pancreatic lipomatosis in cystic fibrosis – CT
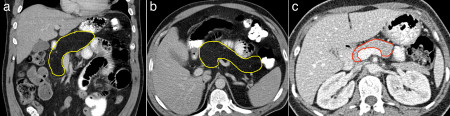
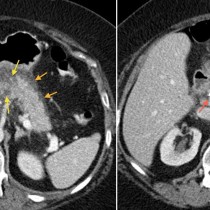
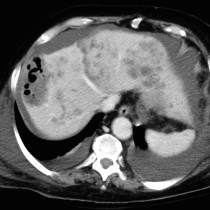
One of the most common manifestations of cystic fibrosis (CF) on abdominal imaging is fatty replacement of the pancreas (lipomatosis), a typical example of which is shown here. The normal dense pancreatic parenchyma has been completely replaced by low density fat, outlined in yellow on coronal CT image (a) and transverse CT (b). A normal pancreas is shown in image (c) for comparison, outlined in red – note how the pancreas in the CF patient is also quite enlarged when compared to the normal example. Other potential abnormalities we may encounter in the pancreas in CF patients include calcifications (due to chronic pancreatitis) and an entity called pancreatic cystosis, where the gland is replaced by multiple cysts.
There is a multitude of additional complications of CF for which we are frequently asked to perform abdominal ultrasound, CT and MRI, including: fatty infiltration of the liver, portal hypertension, cirrhosis, gallstones, distal intestinal obstruction syndrome (DIOS), intussusception, colonic structures and gastrointestinal malignancies. These conditions are being seen with increasing frequency as the life expectancy of patients with CF continues to increase.