Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) – HCC
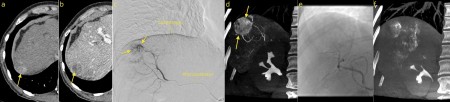
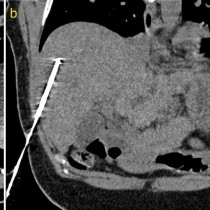
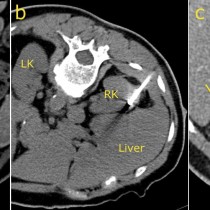
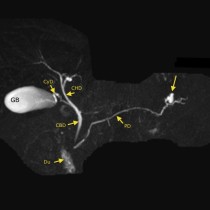
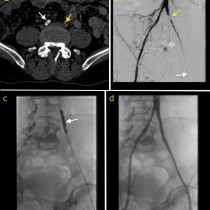
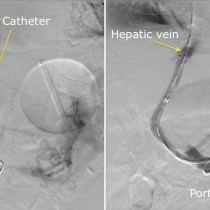
Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). This 49 year old man has HCV cirrhosis and developed a HCC in the right lobe of his liver. The arterial phase of his four-phase liver CT shows a hypervascular lesion, image (a), arrow. Typical of HCC, on the portal venous phase, image (b), the lesion demonstrates ‘washout’, becoming lower density than the surrounding liver parenchyma. TACE was requested. On image (c), a selective catheter has been inserted into the hepatic artery, and a microcatheter advanced into the branch supplying the tumour (which is visible as a ‘blush’ of contrast on this angiogram, arrows). Our IR fluoroscopy equipment can also acquire CT images; image (d) is an example of this and better demonstrates the hypervascular HCC (arrows). The arterial branch was then occluded using embolic material that is coated with a chemotherapeutic agent. The final angiographic and CT images, (e) and (f), show a dramatic reduction in the blood supply to the tumour.